A core–shell structured magnetic Ag/AgBr@Fe2O3 composite with enhanced photocatalytic activity for organic pollutant degradation and antibacterium
Abstract
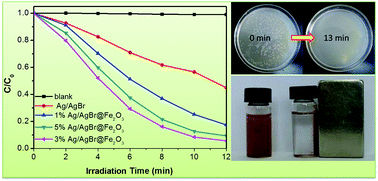
A core–shell structured magnetic Ag/AgBr@Fe2O3 composite was synthesized through a facile solvothermal method. Powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and ultraviolet-visible absorption spectroscopy (UV-vis) were applied to characterize the structures and properties of the as-prepared samples. The results indicate that Fe2O3 was coated on the surface of Ag/AgBr and heterostructures were formed. Electrochemistry analysis and photoluminescence (PL) spectra analysis indicate that the introduction of Fe2O3 could improve electron and hole separation efficiency. The photocatalytic activity of the Ag/AgBr@Fe2O3 composites was evaluated by using organic dye methyl orange (MO), endocrine disrupting chemical bisphenol A (BPA) and Escherichia coli (E. coli) as the target pollutants. The as-prepared Ag/AgBr@Fe2O3 composites exhibited much higher photocatalytic activities than pure Ag/AgBr, which was attributed to the effective charge separation of the Ag/AgBr@Fe2O3 composite. In addition, the as-prepared Ag/AgBr@Fe2O3 composite has magnetic properties, therefore after the photocatalytic reaction, it can be quickly separated from solution by an extra magnetic field. Trapping experiments and ESR analysis indicate that the h+ and ˙O2− are the main active species for the photocatalytic degradation. A possible Z-scheme pathway photocatalytic mechanism was proposed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...