Rationally developed core–shell polymeric-lipid hybrid nanoparticles as a delivery vehicle for cromolyn sodium: implications of lipid envelop on in vitro and in vivo behaviour of nanoparticles upon oral administration†
Abstract
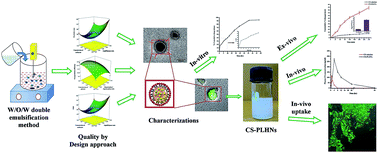
In the present study, cromolyn sodium (CS), a highly water soluble molecule was encapsulated into rationally designed, core–shell polymeric-lipid hybrid nanoparticles (PLHNs) for enhancing its oral bioavailability, by improving its intestinal permeability through lymphatic uptake. The CS encapsulated PLGA–lecithin based core–shell PLHNs (CS–PLHNs) were engineered by a double emulsification solvent evaporation method and optimized using a response surface methodology based “Quality by Design” approach. The Box–Behnken experimental design was imperatively enforced to enhance encapsulation of CS inside PLHNs without compromising particle size. Optimized CS–PLHNs exhibited a particle size of 227 ± 3.8 nm and EE of 57.8 ± 1.32% with unimodal size distribution. The physico-chemical characterizations of CS–PLHNs suggested the encapsulation of CS in an amorphous form inside PLHNs without any interactions. The morphological studies pointed towards the existence of smooth, spherical core–shell architecture of CS–PLHNs, which extended release up to 48 h by a controlled diffusion process. The optimized CS–PLHNs exhibited remarkable stability at different environmental conditions as well as in biological milieu. An ex vivo intestinal permeation study showed that the permeation of CS was significantly improved by encapsulating it inside PLHNs compared to that of pure CS, which was additionally confirmed by the in vivo intestinal uptake study using confocal microscopy. A pharmacokinetic study in rats further exhibited 11.9 fold enhancement in the oral bioavailability of CS after its incorporation into PLHNs. In a nutshell, PLHNs can serve as a superior therapeutic carrier system by imparting lipophilicity to potentially obtain the high oral bioavailability of CS, which can further be extended towards numerous hydrophilic drug molecules.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...