Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):polystyrene sulfonate zirconium(iv) phosphate (PEDOT:PSS–ZrP) composite ionomeric membrane for artificial muscle applications
Abstract
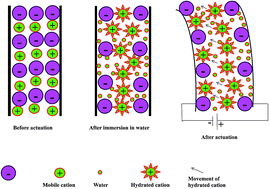
The PEDOT:PSS–ZrP ionomeric actuator was developed for artificial muscle applications. The polyvinyl chloride (PVC) based (PEDOT:PSS) Zr(IV) phosphate composite ionomeric membrane (PVC–PEDOT:PSS–ZrP) was successfully synthesized by a solution casting technique. Various instrumental techniques including thermogravimetric analysis/differential thermal analysis/differential thermogravimetry (TGA/DTA/DTG), energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) analysis, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy were used to characterize the PVC–PEDOT:PSS–ZrP ionomeric material. Membrane properties were evaluated in terms of ion exchange capacity, cyclic and linear sweep voltammetry, water uptake, water loss and proton conductivity. The tip displacement of the PVC–PEDOT:PSS–ZrP composite ionomeric membrane was also studied. The composite ionomeric membrane showed excellent displacement under an applied voltage. Therefore, a composite ionomeric membrane was found to be suitable for bending actuation applications in artificial muscles.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...