Fluorescent nanothermometers based on mixed shell carbon nanodots†
Abstract
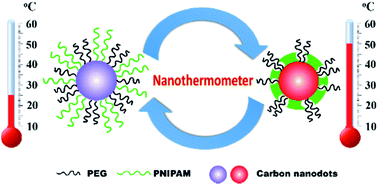
A novel kind of nanothermometer was prepared, which has potential to monitor the temperature variation in the nano regime. The nanothermometer was based on biocompatible fluorescent carbon nanodots (CDs) via one-step microwave assisted synthesis, and two kinds of polymers, including thermo-sensitive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM) and non-thermo-sensitive polyethylene glycol (PEG), were used simultaneously to modify the CDs. Therefore, the as-prepared nanothermometer possesses a CD core and a mixed shell consisting of PEG and PNIPAM chains. The elaborately-designed nanostructure endows the nanothermometer with both temperature sensing capacity and the solution stability. When heating up above the lower critical solution temperature (LCST) of PNIPAM, hydrophobic phase transition occurred to PNIPAM, and the nanothermometer evolved into the core–shell-corona structure, with a freshly-formed and collapsed PNIPAM shell. Meanwhile, the fluorescence behavior of the nanothermometer changed along with the structure transition reversibly without fluorescence decay. The detection temperature of the nanothermometer is consistent with the LCST of the applied thermo-sensitive polymer passivating agents. Moreover, this nanothermometer can remain stable without aggregation and fluorescence quenching whether below or above the LCST due to the stabilizing effect of the PEG chains. Furthermore, the nanothermometer could be endocytosed by cells with negligible cytotoxic effects. In view of the excellent sensitivity and reversibility, preferable biocompatibility as well as nano-scale structure, this nanothermometer shows great potential applications in intracellular imaging and temperature sensing.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...