pH and temperature responsive redox behavior of biologically important aniline derivatives†
Abstract
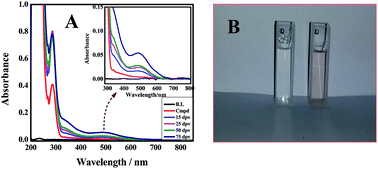
The redox behavior of two biologically important aniline derivatives, 2-(4-aminophenyl) ethanol and 4-aminobenzoic acid was scrutinized in a wide pH range of 2.0–12.0 using modern electrochemical techniques. The results of cyclic voltammetric experiments conducted at different temperatures were used for the evaluation of kinetic and thermodynamic parameters such as diffusion coefficient, heterogeneous electron transfer rate constant, Gibbs free energy, enthalpy and entropy changes. Differential pulse voltammetry was employed for the determination of the acid–base dissociation constant (pKa) and evaluation of the number of electrons and protons involved in redox reactions. The comparatively more rapid and sensitive voltammetric technique, square wave voltammetry allowed the determination of quite a low limit of detection and quantification of the analytes. Computational studies were performed for the identification of the most favorable oxidizable electropores of the compounds and for developing structure–activity relationships in conjunction with the experimental results. On the basis of electrochemical and computational findings a comprehensive redox mechanism was proposed which may provide useful insights about the role by which this class of compounds exert their biological action. The proposed mechanism was found to be in line with the analysis of the product scratched from the electrode surface.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...