In situ synthesis of silver nanoparticles dispersed or wrapped by a Cordyceps sinensis exopolysaccharide in water and their catalytic activity
Abstract
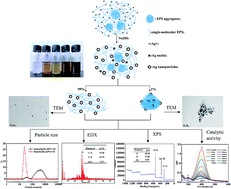
Well-dispersed Ag nanoparticles (AgNPs) were constructed via in situ reduction of Ag+ under the macromolecular environment of a Cordyceps sinensis exopolysaccharide (EPS). The EPS–Ag nanocomposites were characterized in terms of formation, size, morphology, and Ag distribution by UV-VIS, FT-IR, laser light scattering measurements, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Results indicated that the AgNPs in the EPS microenvironment were present in two forms: 99% of small-sized AgNPs (∼5.0 nm in diameter) uniformly dispersed by single-molecular EPS and 1% of aggregated EPS–Ag nanocomposites (∼300 nm in diameter). The interactions between the OH groups of the EPS and AgNPs (C–O–Ag bonds) substituted for inter- and intra-molecular interactions in native EPS, leading to good dispersion of AgNPs in the EPS matrix. Meanwhile, only a few EPS aggregates wrapped many small-sized AgNPs to form large-sized EPS–Ag nanocomposites through strong physical adsorption to O atoms of other EPS aggregates on the surfaces of AgNPs. Additionally, the introduction of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) would facilitate the aggregation of AgNPs in the aqueous system. This work not only provides a simple and efficient approach to construct well-dispersed AgNPs in the aqueous system, and demonstrates the crucial role of the EPS as a biopolymer template for dispersion, stabilization and size control of AgNPs, but also finds the EPS–Ag nanocomposites can serve as a good catalyst for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol to 4-aminophenol by NaBH4. The catalytic reduction had a pseudo-first-order rate constant of 1.26 × 10−3 s−1 and an activity parameter of 15.75 s−1 g−1.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...