A synthetic peptide inhibits human ovarian cancer cell motility†
Abstract
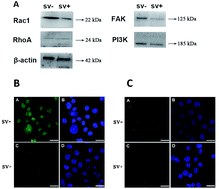
Phage display libraries have been commonly used to identify recognition sites and antigen–antibody binding systems in tumor cells since the 1990s. In the previous study, we isolated a 12-mer binding peptide SVSVGMKPSPRP (SV-peptide) while isolating human ovarian cancer cells (SK-OV-3) using a random phage display library. Therefore, we tested the specific binding and anticancer properties of the SV-peptide with respect to cell viability and motility. The peptide-binding assay showed the immunofluorescent staining intensity of tumor cells (A2780, A549 and SK-OV-3) > control cells (HUVEC). Monolayer scratch healing and Transwell transmigration assays showed that the SV-peptide inhibited the migration of all three cancer cell types but not HUVEC. The mechanism involves a suppression of cytoskeletal F-actin filament arrangement into filopodia and lamellipodia through downregulation of Rac1 but not RhoA. The FAK–PI3K signaling pathway was also affected by the peptide. Western blot analysis revealed a downregulation of FAK, but not of PI3K, after 24 h incubation of SK-OV-3 cells with the SV-peptide. Metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) was also downregulated by the SV-peptide. Finally, the viability of cancer cell lines (SK-OV-3 and A549) decreased in the presence of the SV-peptide after 48 h. Transmission electron microscopy of the SV-peptide-exposed cancer cultures showed extensive vacuolization, swollen mitochondria, and rough endoplasmic reticulum. Thus, the SV-peptide has some certain application prospects in the tumor therapy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...