A novel nanocomposite for bone tissue engineering based on chitosan–silk sericin/hydroxyapatite: biomimetic synthesis and its cytocompatibility
Abstract
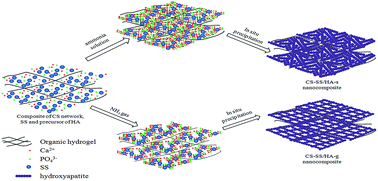
A simple and effective approach was developed to synthesize chitosan–silk sericin/hydroxyapatite nanocomposites by in situ precipitation and two methods of alkali diffusion were carried out in this study. The objective of this paper was to investigate the different properties of the nanocomposites. SEM showed that the rod-like hydroxyapatite particles with a diameter of 20–50 nm were distributed homogeneously within the chitosan–silk sericin matrix, and the formation mechanism was also investigated. The results of FTIR and XRD indicated that the inorganic phase in the nanocomposite was carbonate-substituted hydroxyapatite with low crystallinity. In terms of mechanical properties, chitosan–silk sericin/hydroxyapatite nanocomposites exhibited a higher elastic modulus and compressive strength than that of the chitosan/hydroxyapatite nanocomposites. In vitro cytocompatibility of the nanocomposite was evaluated by CCK-8 assay and SEM through MG63 osteoblast cells cultured on the samples, which demonstrated that they are non-toxic and support cell growth. These results suggest that the chitosan–silk sericin/hydroxyapatite nanocomposites are promising biomaterials for bone tissue engineering.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...