Surface-mediated selective photocatalytic aerobic oxidation reactions on TiO2 nanofibres†
Abstract
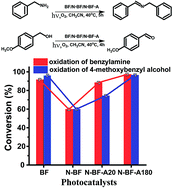
N-doped TiO2 nanofibres were observed to possess lower aerobic oxidation activity than undoped TiO2 nanofibres in the selective photocatalytic aerobic oxidation of benzylamine and 4-methoxybenzyl alcohol. This was attributed to the reduction free energy of O2 adsorption in the vicinity of nitrogen dopant sites, as indicated by density functional theory (DFT) calculations when three-coordinated oxygen atoms are substituted by nitrogen atoms. It was found that the activity recovered following a controlled calcination of the N-doped NFs in air. The dependence of the conversion of benzylamine and 4-methoxybenzyl alcohol on the intensity of light irradiation confirmed that these reactions were driven by light. Action spectra showed that the two oxidation reactions are responsive to light from the UV region through to the visible light irradiation range. The extended light absorption wavelength range in these systems compared to pure TiO2 materials was found to result from the formation of surface complex species following adsorption of reactants onto the catalysts' surface, evidenced by the in situ IR experiment. Both catalytic and in situ IR results reveal that benzaldehyde is the intermediate in the aerobic oxidation of benzylamine to N-benzylidenebenzylamine process.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...