Amphiphilic quasi-block copolymers and their self-assembled nanoparticles via thermally induced interfacial absorption in miniemulsion polymerization†
Abstract
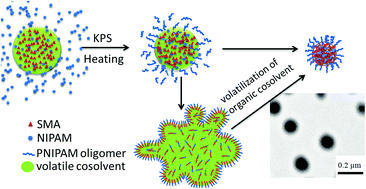
A facile and nontoxic strategy for the preparation of amphiphilic quasi-block copolymers and nanoparticles has been developed utilizing miniemulsion polymerization. By volume phase transition behavior of poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide) (PNIPAM) and thermally induced interfacial absorption, amphiphilic copolymer was generated, which can self-assemble into core–shell nanoparticles in situ. Stearyl methacrylate (SMA) was used as hydrophobic monomer and to form crystalline core, because it has pendent long alkyl side chain and can form crystalline domain to synthesize comb-like polymers. A volatile organic cosolvent was used to enhance the formation process and particles size, and the formation mechanism was investigated. Impacts of cosolvent concentration, monomer feed ratio and polymerization temperature on the morphology and thermal characteristics of particles were studied by DLS, TEM and DSC. 1H NMR, 13C NMR and GPC were carried out to analyze the chemical structure and composition of copolymers. The triads sequence and average block length are analyzed to determine the sequence distribution of copolymers. Volume phase transition temperature (VPTT) of PNIPAM copolymer was first increased to nearly 40 °C with hydrophobic monomer rather than hydrophilic monomer. In addition, hydrophilic property of copolymer and the drug release behavior were studied to understand further applications. These amphiphilic quasi-block copolymers show great potential in the controlled delivery system for drugs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...