Nitrogen- and oxygen-containing activated carbons from sucrose for electrochemical supercapacitor applications†
Abstract
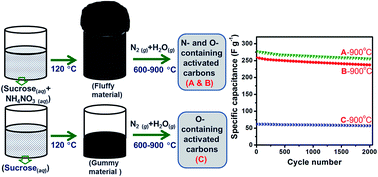
Nitrogen- and oxygen-containing activated carbons have been synthesized from sucrose and ammonium nitrate (AN) by carbonization at different temperatures (600–900 °C) under a flow of nitrogen gas with steam. Another set of carbons has been synthesized without AN. The carbons have been characterized using X-ray diffractometry (XRD), elemental analysis, solid-state 13C nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), thermo-gravimetric analysis (TGA), di-nitrogen adsorption–desorption, Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) techniques. Nitrogen from AN has been found to be incorporated into carbon samples. Electrochemical performances of the carbons have been studied in 1 M sulphuric acid using cyclic voltammetry and galvanostatic charge–discharge cycling. The use of AN favors the formation of carbons with higher surface areas and higher graphitic nature. One of the carbons with a BET surface area of 518 m2 g−1, a nitrogen content of 3% and an oxygen content of 20.4% shows a specific capacitance of 277 F g−1. Carbons obtained using AN show better capacitance than the ones obtained without AN. Higher carbonization temperatures favor the formation of carbon with the higher capacitance values.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...