Fabrication of pH sensitive microcapsules using soft templates and their application to drug release
Abstract
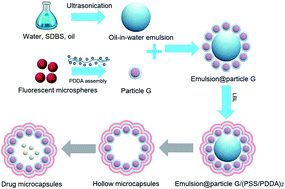
A method based on soft templates for pH sensitive microcapsule fabrication was developed using a layer-by-layer assembly technique. Toluene-in-water emulsion droplets were first stabilized by a surfactant sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate (SDBS). Poly(diallyldimethyl ammonium chloride) modified latex beads were then adsorbed onto the droplet surfaces to make the emulsion more rigid. PSS (poly(sodium 4-styrenesulfonate))/PDDA (poly(diallyldimethyl ammonium chloride)) was assembled alternately onto the emulsion surface to form the microcapsules. Zeta potential analyzer, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), FT-IR, and fluorescence microscopy were used to characterize the samples. The toluene droplet templates were removed by ethanol upon heating. Fluorescein, as the water-soluble model drug, was loaded into the microcapsules. Its release behaviors were investigated as a function of wall thickness and pH. The maximum release percentage 61% was obtained after 36 hours at 37 °C at pH 7 with one double layer capsule. The capsule itself is nontoxic, while 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) loaded capsules killed 64.18% SK-RC-2 cells at a concentration of 17 μM at pH 7, which shows the great potential of this type of microcapsule in cancer chemotherapy. Olive oil and liquid paraffin were used to replace the toluene for forming soft templates in order to obtain microcapsules which are suitable for loading hydrophobic drugs. Sudan-1 was chosen as a hydrophobic model drug and 25% release was obtained after 36 hours at 37 °C.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...