The interaction of QDs with RAW264.7 cells: nanoparticle quantification, uptake kinetics and immune responses study†
Abstract
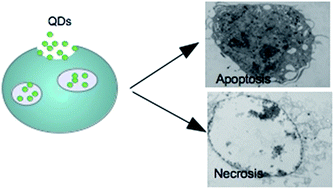
Fluorescent semiconductor nanocrystals called quantum dots (QDs) have been proposed as a prominent bio-imaging tool due to their exceptional optical properties. Typically the core size is not greater than 10 nm, thus QDs don't obey models successfully developed and proved on practice for large particles (40–200 nm). This makes it difficult to predict the behaviour of such small yet reactive species in physiological media. Despite the benefits provided by QDs, the challenge of quantifying altered intracellular components remains complicated, and is not clearly investigated, due to interaction of nanoparticles with different cellular compartments. The goal of this work is to investigate uptake kinetics of small green-emitting TGA-capped CdTe QDs with diameter as small as 2.1 nm and to quantify their accumulation inside the cells over the time by flow cytometry. The effect on RAW264.7 monocyte–macrophage cell function and viability also was studied, as monocytes play an important role in innate immunity. The optimal parameters (QD concentration, exposure time, cell activation status) were found; the tested nanoparticles are proven to be applied in short-term assays due to their quick ingestion and accumulation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...