Silarylene-containing oligo(ether-amide)s based on bis(4-(4-amino phenoxy)phenyl)dimethylsilane. Effect of the dicarboxylic acid structure on some properties
Abstract
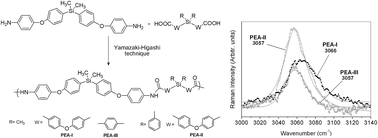
Oligo(ether-amide)s (PEAs) based on diphenylsilane and oxyphenyl units were synthesized through a Yamazaki–Higashi phosphorylation polyamidation technique. Thus, three new aromatic monomers were synthesized and characterized: a di(ether-amine), bis(4-(4-aminophenoxy)phenyl)dimethylsilane, and two dicarboxylic acids, bis(4-(4-carboxyphenoxy)phenyl)dimethylsilane and bis(4-(4-carboxyphenoxy)phenyl)diphenylsilane. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry analyses show that the average molecular masses of the PEAs ranged from 1334 to 2097 m/z. The UV-vis technique was used to determine the optical band gap (Eg) of the oligomers. These values were between 3.91 and 4.57 eV. On the other hand, the conductivity of the samples was measured in the solid state (film) through the “four point method” showing a slight conductor behavior (13.3 and 5.0 S cm−1). Determination of fluorescence emission peaks showed two absorption bands. The first peak is related to a lesser electron-donating nature from an amide group, while the second peak was attributed to the polar solvent. Raman spectroscopy was used to determine the functional group in order to corroborate the structure and the crystallinity degree of the PEAs. Microstructural analyses of the samples were developed by using grazing incidence X-ray diffraction, showing amorphousness in the system studied. AFM micrographs showed that all the samples present certain porosity. On the other hand, the incorporation of flexibility inducing oxyether linkages affected positively the solubility of the PEAs in common organic solvents, and also decreased significantly the values of the glass transition temperature (Tg) and increased the transparency in the UV-vis region. In all cases, the thermal decomposition temperature values (TDT10%) were above 400 °C.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...