Synthesis and bioactivity of novel xanthone and thioxanthone l-rhamnopyranosides†
Abstract
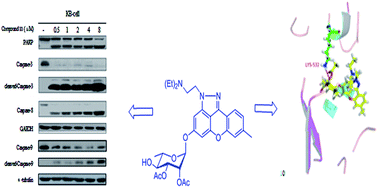
A series of xanthone and thioxanthone rhamnopyranosides were designed and synthesized. Their in vitro cytotoxicity and topoisomerase inhibitory activity were evaluated. The bioassay results indicated that the introduction of the 2,3-di-O-acetyl-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl moiety to anthracene was helpful to improve the cytotoxicity in vitro. The modifications of anthracene had an important effect on the tumor cell growth inhibitory activity. Interestingly, consistency was observed between the cytotoxicity and topo I activity in these anthracene analogs, suggesting that the incorporation of either a polymethyleneamine side chain or a pyrazole ring into the anthraquinone chromophore was able to enhance topo I inhibitory activity as well as cytotoxicity simultaneously. Among them, compound 11 as a new lead compound was discovered, which showed wide in vitro cytotoxicity against 12 tumor cell lines and potential antimultidrug resistance capability. It was proved that compound 11 could induce cell apoptosis in KB cells via both extrinsic and intrinsic pathways. Flow cytometric analysis exhibited that treatment of KB cells with compound 11 led to cell apoptosis accompanied by cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase. Furthermore, compound 11 caused a significant and dose-dependent inhibition of topoisomerase I catalytic activity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...