Yellow electrophosphorescent devices with hosts containing N1-(naphthalen-1-yl)-N1,N4-diphenylnaphthalene-1,4-diamine and tetraphenylsilane units†
Abstract
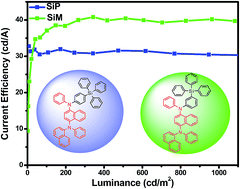
Two novel host materials, N1-(naphthalen-1-yl)-N1,N4-diphenyl-N4-(4-(triphenylsilyl)phenyl) naphthalene-1,4-diamine (SiP) and N1-(naphthalen-1-yl)-N1,N4-diphenyl-N4-(3-(triphenylsilyl) phenyl)naphthalene-1,4-diamine (SiM), were synthesised by incorporating a hole-transporting moiety, N1-(naphthalen-1-yl)-N1,N4-diphenylnaphthalene-1,4-diamine (NPNA2) and typical electron-transporting tetraphenylsilane moiety. SiP and SiM materials exhibit high thermal and morphological stability with a glass transition temperature higher than 110 °C and decomposition temperature above 350 °C. Using Ir(bt)2(acac) (bis(2-phenylbenzothiozolato-N,C2′)iridium(acetylacetonate)) as an emitter, yellow phosphorescent organic light-emitting diodes of ITO/TAPC (1,1-bis[4-(di-p-tolylamino)phenyl]cyclohexane, 40 nm)/host: Ir(bt)2(acac) (15 wt%, 20 nm)/TmPyPB (1,3,5-tri(m-pyrid-3-yl-phenyl)benzene, 40 nm)/LiF (1 nm)/Al (100 nm) show maximum current and power efficiency of 40.81 cd A−1 and 33.60 lm W−1 with low efficiency roll-off. The current efficiency of 40.10 cd A−1 is still observed at the practically useful brightness value of 1000 cd m−2.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...