Role of exchange and correlation in the real external prediction of mutagenicity: performance of hybrid and meta-hybrid exchange–correlation functionals†
Abstract
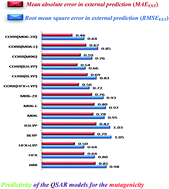
Quantum-mechanical exchange and correlation interactions between electrons are quite crucial in deciding molecular geometry and properties. Such electronic interactions can have a significant role in the reliability of a quantitative structure–activity relationship (QSAR) because the biological activities of the chemicals can be described as a function of the molecular structure through the QSARs which are routinely based on the quantum-mechanical molecular descriptors. In this work, we present a detailed analysis of the effect of the quantum-mechanical exchange and correlation on the internal stability and external predictivity of a QSAR model based on the quantum-mechanical molecular descriptors while modeling the mutagenic activity of a set of 51 nitrated-polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). For this, various molecular descriptors are computed using electronic structure methods such as the Hartree–Fock (HF) method, and density functional theory (DFT) employing only the exchange functionals (HFX, B88), pure exchange and correlation functionals (HFX + LYP, BLYP), hybrid (B3LYP), meta (M06-L), and meta-hybrid (M06, M06-2X) exchange–correlation (XC) functionals. To further analyze the role of electron-correlation, QSAR models are also developed using the descriptors incorporating mainly the effect of electron-correlation. The external predictivity of the developed models is assessed through state-of-the-art external validation parameters employing an external prediction set of compounds. A comparison of the quality of the models developed with the descriptors computed using different electronic structure methods revealed that the exchange interactions are quite critical along with the electron-correlation in modeling the mutagenicity. Notably, for most of the models, electron-correlation based descriptors are found to be highly reliable when computed using the hybrid XC functionals, particularly B3LYP and M06-2X.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...