Surface modification of intraocular lenses with hyaluronic acid and lysozyme for the prevention of endophthalmitis and posterior capsule opacification
Abstract
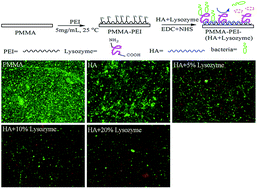
Posterior capsule opacification is one of the complications of cataract surgery caused by the adhesion and reproduction of residual human lens epithelial cells (HLECs) on the posterior capsule. Infectious endophthalmitis is another common complication due to bacterial colonization and biofilm formation. Hyaluronic acid–lysozyme (HA–lysozyme) composite coating was covalently grafted on the surface of PMMA intraocular lenses by reaction with N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) and 1-etil-3-(3-dimetilaminopropil) carbodiimida (EDC). Measurements of water contact angle and AFM revealed that the coating created a highly hydrophilic surface with low roughness. Adherences of S. aureus and HLECs on PMMA with HA or HA–lysozyme coating were significantly reduced due to the hydrophilic property of HA. Bactericidal activity of HA–lysozyme coatings, measured by SEM and LIVE/DEAD bacterial viability kit, was remarkably effective against S. aureus owing to the component of lysozyme. The achievement of the HA–lysozyme composite coating with anti-adhesive and antibacterial properties can potentially be widely used on surface modification of PMMA intraocular lenses and other biomedical implants.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...