Interactions in globular proteins with polyampholyte: coacervation route for protein separation†
Abstract
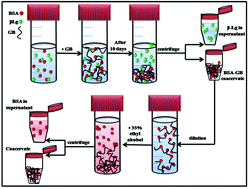
In this work, we report exclusive separation of Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) from a solution where this protein was present with β-lactoglobulin (β-Lg) in 1 : 0.75 (w/v) ratio at their common isoelectric pH (5 ± 0.02). A polyampholytic polypeptide Gelatin B (GB) also having the same pI was used to extract protein (BSA or β-Lg) molecules selectively from this solution through a process called complex coacervation. In our study, the protein-rich condensate, called coacervate, comprised of GB–BSA complexes while the supernatant mostly contained β-Lg molecules. For the separation of BSA from BSA–GB coacervate, we used ethyl alcohol, which removed the BSA to the supernatant. The differential binding affinity of BSA versus β-Lg to GB chains was established through fluorescence quenching and fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) studies. The BSA–GB binding protocol followed a surface selective patch binding mechanism and these results were obtained from an array of experimental methods such as UV-vis and fluorescence spectroscopy, small angle neutron scattering (SANS), FTIR and circular dichroism spectroscopy. Herein, it is clearly established that selective coacervation at pI can be used as a method for protein separation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...