Amperometric glucose sensor based on boron doped microcrystalline diamond film electrode with different boron doping levels
Abstract
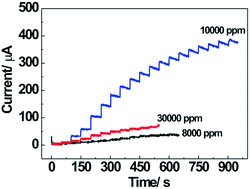
Boron doped microcrystalline diamond (BDMD) films with different boron concentrations were deposited on Si (100) by microwave plasma chemical vapor deposition in a gas mixture of CH4/H2/TMB. The influence of boron concentration on the surface morphology, microstructure, and electrochemical properties of BDMD film electrodes was studied. It was found that boron dopants play an important role in the structural quality and electrochemical properties of BDMD film electrodes. The increase of doped boron concentration results in the reduction of diamond grain size and the domination of two peaks located at approximately 500 and 1220 cm−1 in the Raman spectra. Marked differences are observed for BDMD film electrodes with various boron concentrations in impedance characteristics. The electron transfer reaction on BDMD film electrodes becomes faster and reversibility is improved with the increase of boron concentration. Meanwhile, the electrochemical reactions on the BDMD film electrodes become a diffusion controlled process. The non-enzymatic glucose sensors based on as-prepared BDMD film electrodes were developed. The glucose oxidation peak position and current density are dependent on the B/C ratio for the BDMD film electrodes. The results show that appropriate boron doping concentration can improve the conductivity and electrocatalytic activity of BDMD film electrodes. The BDMD film electrode with B/C ratio of 10 000 ppm exhibits the highest sensitivity of 96.88 μA mM−1 cm−2, lowest detection limit of 0.018 mM and widest linear range of 0.1 to 5 mM. The developed non-enzymatic glucose sensors based on as-prepared BDMD film electrodes demonstrate selective detection of glucose in alkaline solution containing interfering species of ascorbic acid and uric acid.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...