Functionalized nanospheres for efficient sequestration of cadmium ions
Abstract
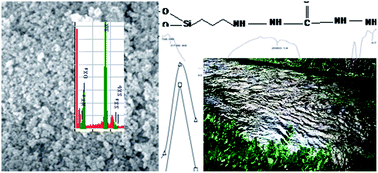
This manuscript reports the synthesis, characterization and the subsequent application of thiosemicarbazide functionalized nanosilica spheres in Cd(II) ion sequestration. The spheres are developed by the sol–gel method, activated with an organosilane precursor and then conjugated with thiosemicarbazide using a one-step Mannich reaction. The successful grafting is confirmed using FTIR, TGA, SEM and EDX analyses. Cd(II) ion sequestration from aqueous solutions is studied exhaustively in competitive and noncompetitive environments in batch experiments using the radiotracer technique. The sorption process is fast and can reach equilibrium in 40 minutes with 98% Cd(II) ion sequestration at pH 7 following first-order kinetics (K = 0.0465 min−1). The sorption data follow the Langmuir, Freundlich and Dubinin–Radushkevich (D–R) isotherms and its characteristic constants were computed to be as follows: N = 10 mmol g−1 and b = (0.1) × 104 dm3 mol−1, 1/n = 0.64 and of Cm = 0.04 mmol g−1 and D–R constants, i.e. β = −0.00064 kJ2 mol−2, Xm = 1.8 mmol g−1 and Es = 8.8 kJ mol−1. The sorption of Cd(II) ions onto nanospheres is spontaneous (ΔG = −1050.00 J mol−1 K−1) and endothermic in nature (ΔH = 2.45 J mol−1 K−1). The Cd(II) ions sequestration is highly reduced in the presence of cyanide, EDTA, aluminum and nickel ions. The sorbent is regenerable and can be used several times.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...