Smart electrospun fibrous scaffolds inhibit tumor cells and promote normal cell proliferation
Abstract
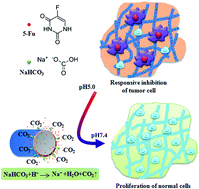
A smart and stable electrospun fibrous drug carrier was fabricated to release an incorporated drug in response to the local presence of acid and to provide a favourable micro-environment for tissue regeneration. To fabricate the electrospun fibrous scaffolds responsive to the local pH variation, sodium bicarbonate, a component of acid response, was facilely incorporated into drug-loaded electrospun fibers by co-electrospinning. The analysis of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, Fourier-transform infrared spectrometry, X-ray diffraction, Differential scanning calorimetry and water contact angles demonstrated that the sodium bicarbonate was successfully incorporated into the electrospun fibers. The in vitro drug release results showed that the release rate of an anti-cancer drug 5-fluorouracil in an acidic environment from the electrospun fibrous scaffolds was proportional to the concentration of sodium bicarbonate, and the structure of the electrospun fibrous scaffolds was well maintained before and after the drug release. The acid-responsive release of 5-fluorouracil for a short time was found to effectively inhibit osteosarcoma cell growth, and the electrospun fibrous scaffolds with long-term stability supported fibroblast adhesion and proliferation, indicating the potential for subsequent tissue regeneration.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...