Unique impact behavior and toughening mechanism of the polypropylene and poly(ethylene-co-octene) alternating multilayered blends with superior toughness†
Abstract
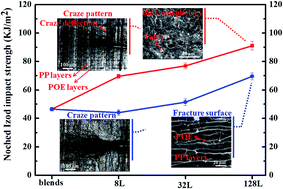
In this study, a novel approach is proposed to significantly toughen polypropylene (PP) by fabricating PP and poly(ethylene-co-octene) (POE) into alternating multilayered blends instead of conventional blends. POM, SEM, polarized-FTIR, DSC and XRD were performed to investigate and characterize the microstructure of the alternating multilayered and conventional blends. The crack-initiation term, impact fracture surface and bulk morphologies beneath the fracture surface are inspected in order to understand the differences in the impact behaviors of the alternating multilayered blends and the conventional blends. The results show that the unique multilayered structure has a great advantage in toughening PP. The notable improvement of the toughness of the alternating multilayered blends is ascribed to the synergetic effects of the interfaces' delaminations, craze deflection, larger subcritical damage zone (stress whitening zone) and the combination of the voids and deformation during the fracture process. Moreover, the alternating multilayered blends exhibit high toughness with a low POE content; thus, this work also offers a new method to toughen the materials without an obvious sacrifice of their strength.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...