The synthesis and characterization of carboxybetaine functionalized polysiloxanes for the preparation of anti-fouling surfaces†
Abstract
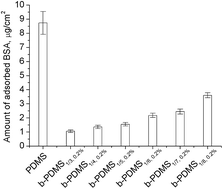
Nonspecific protein adsorption and bacterial adhesion have caused serious problems in biomedical devices, marine engineering, membrane separation and many other areas. In order to develop a water-soluble bio-adhesion resistant material, a series of novel zwitterionic polymers, carboxybetaine functionalized polysiloxanes (PDMS-g-CB), were synthesized via a three-step procedure. FT-IR and NMR were used to characterize the chemical structures of PDMS, and the solution properties (i.e. CMC) and biological characteristics were investigated. The high biocompatibility of PDMS-g-CB was demonstrated by hemolysis assay, skin irritation evaluation and acute oral toxicity testing. To evaluate the anti-fouling and hydrophilic properties of PDMS-g-CB, it was blended with PDMS elastomer to form films (b-PDMS). Water contact angle and ATR-FTIR measurements revealed that the hydrophobic PDMS surfaces were converted to hydrophilic surfaces after the introduction of PDMS-g-CB. The anti-fouling properties of b-PDMS were evaluated by protein adsorption and bacterial adhesion tests. Results showed that the amount of adsorbed protein and bacteria adhesion were significantly reduced compared with the untreated PDMS. These findings suggest that PDMS-g-CB is a biocompatible and promising material for the construction of anti-fouling surfaces.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...