Immobilization of palladium catalyst on magnetically separable polyurea nanosupport†
Abstract
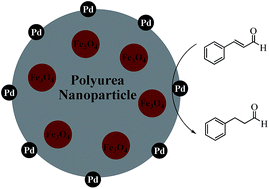
This work describes a method for preparing magnetic polyurea nanoparticles (PU NPs) and their utilization as a catalyst support. The method is based on entrapment of hydrophilic magnetic nanoparticles within the polyurea matrix. The synthetic process of these magnetic polyurea nanoparticles is based on oil-in-oil nanoemulsification of an organic polar phase comprised of N,N-dimethylacetamide (DMAc), 2,6-diaminopyridine and ionic liquid modified magnetite nanoparticles (MNPs-IL), in heptane containing a suitable surfactant. This was followed by interfacial polycondensation reaction between an isocyanate monomer, polymethylenepolyphenyl isocyanate (PAPI 27), and the amine monomer producing magnetically separable polyurea nanoparticles. Subsequently, these particles were employed as a catalyst nanosupport. Two catalytic systems based on the encapsulation of Pd(OAc)2 within magnetic PU NPs or their adsorption on the surface of these particles were produced and subjected to hydrogenation reactions and selective hydrogenations of α,β-unsaturated compounds. Pd(OAc)2 adsorbed on the surface of the magnetic PU NPs demonstrated high catalytic activity and selectivity, which was superior to the conventional catalyst Pd/C or palladium nanoparticles supported directly on the surface of magnetite nanoparticles. The catalyst was easily recovered from the reaction mixture by applying an external magnetic field and recycled over five times without observing any significant loss in its catalytic efficiency.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...