Green bionanocomposites from high-elasticity “soft” polyurethane and high-crystallinity “rigid” chitin nanocrystals with controlled surface acetylation†
Abstract
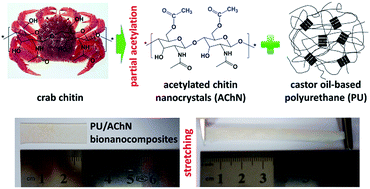
Castor oil-based polyurethane bionanocomposites with improved mechanical properties were prepared by the introduction of crab chitin nanocrystals from partial surface acetylation. Through controlled acetylation, some of the hydrophilic hydroxyl groups on the nanocrystals were replaced by hydrophobic acetyl groups in order to enhance the compatibility between the chitin nanoparticles and polyurethane; and some of the hydroxyl groups were preserved on the surface of nanocrystals for the purpose of rigid network formation among chitin nanoparticles. The presence of acetylated chitin nanocrystals at moderate concentration (6 wt%) will significantly promote the nano-reinforcing effect in composites, and simultaneously improved the strength, stiffness and toughness of thermoplastic polyurethane-based nanocomposites. Meanwhile, derived from the restriction of rigid nanocrystals to soft segments, the glass transition temperatures of the nanocomposites surprisingly increased with the higher loading levels of acetylated chitin nanocrystals. More importantly, this study provided a strategy for the discussion of synergistic effects and “trade-off” of adequate dispersion, network formation and interfacial adhesion of rigid nanoparticles in soft polymeric matrices, by means of structure and properties analysis of semi-transparent polyurethane/acetylated chitin nanocrystals composites.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...