Cu2ZnSnS4 thin film solar cell utilizing rapid thermal process of precursors sputtered from a quaternary target: a promising application in industrial processes
Abstract
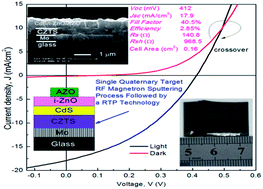
Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) thin films have been attracting considerable attention as candidates for new photovoltaic materials. As a typical vacuum process, a sputtering stacked metallic layer followed by a conventional slow thermal process (STP) is usually used. This method is complex and time-consuming. Furthermore, the volatilization of Zn and Sn elements is significant during the STP process. To simplify the CZTS fabrication process and solve the element volatilization problem, in this work CZTS thin film was fabricated using a single quaternary target Radio-Frequency (RF) magnetron sputtering process followed by a rapid thermal process (RTP). The effects of sulfurization temperature on the properties of CZTS thin films have been studied. The compositional analysis shows that a combination of a single target sputtering process and the RTP technique can significantly reduce the volatilization of Zn and Sn elements compared to the conventional STP process. The results of X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns and Raman scatting spectra show that the sulfurized CZTS thin films have a polycrystalline kesterite crystal structure. If the sulfurization process is performed at lower temperature, a large amount of disorder among the Cu and Zn cations exists in the CZTS thin film which is investigated by using Raman scattering spectra. At 550 °C, the CZTS thin film has high quality of crystallinity with large grain size and dense morphology, its band gap energy is found to be 1.53 eV. The solar cell fabricated with the CZTS absorber grown at an optimized sulfurization temperature of 550 °C shows a conversion efficiency of 2.85% for a 0.16 cm2 area with Voc = 412 mV, Jsc = 17.9 mA cm−2, and FF = 40.5%. These results show that this process is suitable for the growth of kesterite CZTS solar cell absorbers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...