Silicon carbide whiskers reinforced akermanite scaffolds for tissue engineering
Abstract
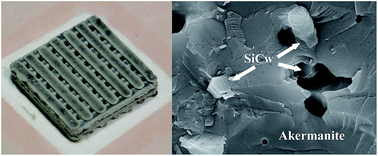
The poor mechanical properties of akermanite (AKM), especially fracture toughness, limits its applications in bone tissue engineering, although it possesses favorable biological performance. In this research, silicon carbide whiskers (SiCw) are added in order to reinforce AKM scaffolds with controllable porous structures fabricated by selective laser sintering (SLS). The mechanical properties, microstructure and toughening mechanisms are analyzed. The results indicate that the compressive strength and fracture toughness increases with increasing SiCw from 5 to 20 wt.%, and then decreases when more SiCw are incorporated. The strengthening and toughening mechanisms are attributed to interface debonding, whisker fracture and whisker pull-out, and the main fracture mode becomes transgranular fracture. Moreover, the phase composition of SiCw remains constant, confirmed by X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis. The bioactivity and degradation behaviour of the scaffolds were evaluated by soaking them in simulated body fluid (SBF). The results show that the composite scaffolds with 20 wt.% SiCw exhibits good apatite-mineralization ability and a moderate degradation rate in SBF medium. Moreover, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis, MTT assay and alizarin red staining of human bone marrow stromal cells (hBMSCs) seeded scaffolds confirm the stem cell attachment, viability, proliferation and differentiation on the scaffolds. Thus, the overall study proves that SiCw reinforced AKM scaffolds have the potential to be used in bone tissue engineering.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...