Electroless nickel coated nano-clay for electrolytic removal of Hg(ii) ions
Abstract
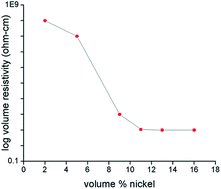
The footprint existence and accumulation of cataclysmic Hg(II) ions in aqueous media poses a severe threat to biological ecosystems and necessitates immediate measures for its regulation. In this context, we have elucidated an electrolytic removal of Hg(II) ions from a prepared solution, which is akin to an effluent system, utilizing novel electroless nickel coated nanoclay electrodes. The dependence of adsorption efficiency on several parameters, including the initial pH (pH = 3 to 8), initial metal ion concentration (25–100 mg L−1), amount of nickel coated on nanoclay, has been studied. The optimized removal percentage of 70% was recorded at pH 6, when distance between the electrodes was 4 cm and a current density ranging from 2–2.5 A dm−2 was passed for duration of 60 minutes. No considerable differences in removal efficiency were registered with varying initial metal ion concentration (25–100 mg L−1). Moreover, the removal efficiency was observed to be high at slightly acidic pH (pH = 6), however, in a highly acidic solution (pH = 3–4), low adsorption efficiency was recorded due to electrostatic repulsion caused by H+ ions. Nickel coating over the nanoclay of 15% (v/v) or greater was found to exhibit an optimised conductivity. SEM and FESEM analysis affirmed the uniform deposition of nickel over the nanoclay. The uptake of Hg(II) ions predominantly followed pseudo second-order kinetics, which was validated by the high values of regression coefficient at all concentrations, and Freundlich equilibrium isotherm model was observed to be better for predicting equilibrium adsorption based on linearized correlation coefficient (R2 = 0.99).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...