Preparation and characterization of SrTiO3–ZnTe nanocomposites for the visible-light photoconversion of carbon dioxide to methane†
Abstract
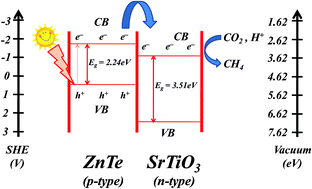
Limited fossil fuel resources and increasingly stringent requirement of environmental protection from major greenhouse gases, including carbon dioxide (CO2), which results directly from the burning of fossil fuels, energy savings and greenhouse-effect alleviation have emerged as major global concerns. The development of an “artificial photosynthetic system” (APS) having both the analogous important structural elements and the reaction features of photosynthesis to achieve solar-driven water splitting and CO2 reduction is highly challenging. Herein, it has been demonstrated that SrTiO3–ZnTe can be utilized as an efficient APS for the photoreduction of CO2 into methane (CH4) under visible-light irradiation (≥420 nm). The results indicate that the combination of ZnTe with SrTiO3 visibly increases the formation of CH4 by efficiently promoting electron transfer from the conduction band of ZnTe to that of SrTiO3 under visible-light irradiation, and thereby demonstrate this to be a promising candidate for the photocatalytic conversion of CO2 into hydrocarbon fuels.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...