Silica prepared in the presence of alkylphosphonium-based ionic liquids and its performance in electrorheological fluids
Abstract
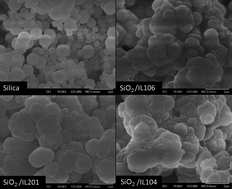
This work highlights the effect of silica particles prepared by a sol–gel process in the presence of different phosphonium-based ionic liquids on the electrorheological behavior of the corresponding suspension in silicone oil. The silica particles were prepared by hydrolysis/condensation of tetraetoxy silane (TEOS) in basic medium and in the presence of three different commercial ionic liquids: tri-isobutyl(methyl)phosphoniumtosylate (IL106), tri(n-butyl)(tetradecyl)phosphonium-dodecylbenzene-sulfonate (IL201) and trihexyl-(tetradecyl)-phosphonium-bis-2,4,4-(trimethylpentyl)-phosphinate (IL104). The resulting material was characterized by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), thermo-gravimetric analysis (TGA), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and dielectric properties. The confinement of the ionic liquids inside the silica particles was suggested by thermogravimetric analysis. The presence of ILs also exerts a strong influence on the morphology and imparts good polarization ability to the silica. The electro-rheological response of the corresponding ionogel suspensions in silicone oil was investigated. A significant ER effect was observed for the fluid containing silica prepared in the presence of IL106. In fact, a very good response under the action of an electrical field corresponding to 3 kV mm−1 was achieved, with a shear stress value as high as 1215 Pa. This behavior may be attributed to the presence of the IL confined in the silica particles and also to the peculiar morphology which favors the formation of a columnar structure to a high extent.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...