Direct electrochemistry and electrocatalysis of glucose oxidase based poly(l-arginine)-multi-walled carbon nanotubes†
Abstract
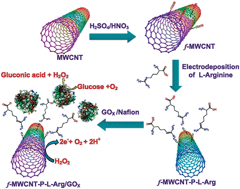
This paper reports a simple and fast approach for the construction of a novel glucose biosensor based on the electro polymerization of a poly-L-arginine film (P-L-Arg) onto functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes (f-MWCNTs)/glassy carbon electrode (GCE) via electrostatic attraction with glycoprotein glucose oxidase (GOx). The morphological and electrochemical properties of the prepared composite were studied by scanning electron microscopy, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, cyclic voltammetry, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. The prepared GOx/P-L-Arg/f-MWCNTs film modified electrode shows a well defined reversible redox couple at a formal potential of −0.45 V (vs. AgCl) with significantly enhanced peak currents corresponding to the direct electrochemistry of the GOx. The direct electron transfer process is a surface-controlled electrode process with a high heterogeneous electron transfer rate constant (ks) of 5.16 s−1. Moreover, this modified electrode was demonstrated to be an efficient glucose biosensor by means of the reductive detection of oxygen consumption. The proposed biosensor possesses excellent analytical parameters for a wide linear range of glucose from 4.0 μM to 6 mM (a correlation coefficient of R2 = 0.9918) with a 5 s response time. The sensitivity of the biosensor is found to be 48.86 μA cm−2 mM−1, its experimental detection limit is 0.1 μM (S/N = 3), the apparent Km is calculated to be 2.2 mM and it also exhibits good storage stability for 25 days. The novel biosensor developed in this study exhibits a fast response, high stability and very good reproducibility.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...