Mild temperature synthesis of gold nanoplates using polyethyleneimine and their improved surface enhanced Raman signal†
Abstract
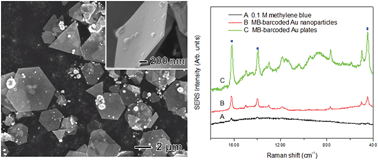
This study explores the facile controlled-synthesis and localized surface plasmonic properties of Au nanoplates. Au nanoplates were synthesized via a reaction of HAuCl4 with branched polyethyleneimine (BPEI) in the presence of urea at a reaction temperature as low as 30 °C. Structural characterizations revealed that the synthesized Au nanoplates had an average lateral size of around 2–8 μm and a thickness of around 40 nm, plus they were highly crystalline in spite of the low reaction temperature. Studies of the growth factors for Au nanoplates showed that the PEI morphology, molar ratio of BPEI/HAuCl4, pH of the reaction solution, and concentration of urea all played important roles in the formation of thin Au nanoplates. With a low BPEI/HAuCl4 ratio or under acidic conditions, thick Au plates were synthesized, whereas Au nanoparticles around 10–20 nm were observed with a high BPEI/HAuCl4 ratio or under basic conditions. When the synthesis was conducted in the absence of urea, thick Au nanoplates were synthesized, indicating that urea can serve as a capping agent for thin Au nanoplates. The resulting Au nanoplates also exhibited an enhanced surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) signal when compared with Au nanoparticles due to their sharp corners and edges.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...