Novel metronidazole-sulfonamide derivatives as potent and selective carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: design, synthesis and biology analysis
Abstract
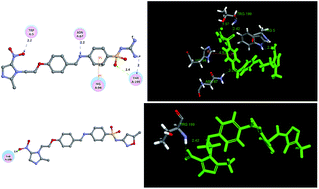
Metronidazole–sulfonamide derivatives 4a–4l, a new class of human carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (hCA), were designed, synthesized, isolated, and evaluated for their ability to inhibit the enzymatic activity of the physiologically dominant isozymes hCA II and the tumor-associated isozyme hCA IX (h = human). Many of these compounds inhibited CA II and IX in the range of 16–137 and 38–169 nM, respectively. Among all the compounds, the most potent inhibitor against hCA II and IX were compounds 4b (IC50 = 16 nM) and 4h (IC50 = 38 nM). Conversely compounds 4e and 4d displayed the most potent growth inhibitory activity against B16-F10 and MCF-7 cancer cell lines in vitro, respectively, with an IC50 value of 150 nM for B16-F10 and 6.5 nM for MCF-7. These metronidazole–sulfonamide derivatives may prove interesting lead candidates to target tumor-associated CA isozymes, wherein the CA domain is located extracellularly. All the new compounds were evaluated for cytotoxicity against human macrophages by MTT assay.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...