Ultrafine PEG-capped gadolinia nanoparticles: cytotoxicity and potential biomedical applications for MRI and luminescent imaging
Abstract
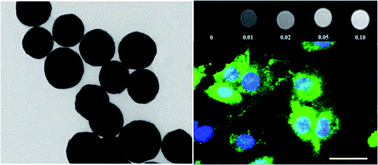
In recent years, magnetic and luminescent nanoparticles (NPs) have attracted considerable attention because of their potential applications in nanomedicine. In this study, bimodal ultrafine polyethylene glycol (PEG)-capped gadolinium oxide NPs doped with erbium ions, which combine both paramagnetic and luminescent properties in a single entity, were synthesized using the urea homogeneous precipitation route. The morphological, chemical and structural properties of the synthesized particles were examined using a range of microscopy and energy-dispersive X-ray techniques. The optical characteristics of the gadolinium oxide NPs were examined by analyzing the room temperature emission spectra, which correspond to various manifold transitions of Er3+. Pilot studies were performed to examine the cytotoxicity and capability of the synthesized NPs for the luminescent labeling of living C2C12 myoblastic cells. The paramagnetic properties of the synthesized particles as a magnetic resonance imaging MRI contrast agent were also assessed. Overall, these synthesized ultrafine PEG-coated Gd2O3:Er3+ NPs can potentially be used in biomedical applications because of their strong positive contrast enhancement in T1-weighted imaging, and intense green emission with near-infrared (NIR, 980 nm) excitation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...