Thin electroconductive hydrogel films by in situ electropolymerization of pyrrole within polyelectrolyte multilayers
Abstract
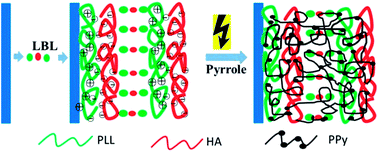
Electroconductive hydrogel (ECH) films have becoming more and more attractive in the field of electro-stimulated response systems and biosensors. Comparatively speaking, the thinner ECH films enable faster response to external stimuli. However, construction of thin ECH films with thickness at the nano-to-micrometer scale is challenging. In the present study, we reported a thin ECH film by in situ electropolymerization of pyrrole within the layer-by-layer (LbL) polyelectrolyte multilayers. Thin poly(L-lysine)/sodium hyaluronate (PLL/HA) multilayers were fabricated. Polypyrrole (PPy) was then prepared by in situ electropolymerization of pyrrole within the multilayers by the galvanostatic method. Chronopotentiometry and an electro-quartz crystal microbalance were used to follow the electropolymerization. The chemical and structural characteristics of the thin ECH film were extensively investigated. Electrical impedance spectroscopy and cyclic voltammetry measurements demonstrated that this (PLL/HA)@PPy film has good electroconductivity with impedance as low as 5 Ω. This thin ECH film could to be a highly desirable candidate for applications in implantable electro-related biomedical devices and biosensors.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...