CuO/Cu2O nanofibers as electrode materials for non-enzymatic glucose sensors with improved sensitivity
Abstract
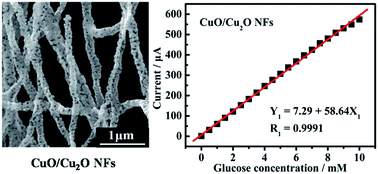
CuO nanofibers (NFs) were fabricated via the traditional electrospinning technique and subsequent thermal treatment processes. Using CuO NFs as precursors and glucose as a reducing agent, CuO/Cu2O NFs, with high surface areas and ultralong one dimensional (1D) nanostructures, were obtained by a partial reduction of CuO NFs. Comparing with pure CuO NFs, CuO/Cu2O NFs, as non-enzymatic electrode materials, showed a much higher sensitivity of 830 μA mM−1 cm−2 and a much wider detection range from 0.5 mM to 10 mM for the amperometric detection of glucose. The excellent electrocatalytic performances could be ascribed to the following advantages: (1) the CuO/Cu2O NFs with Cu(II)/Cu(I) multiple oxidation states system could promote the redox reactions between electrode materials and glucose, and the reactive sites became more active due to the synergic effect; (2) the surface of CuO/Cu2O NFs became smoother after partial reduction, resulting in less adsorption of the intermediates during the oxidation of glucose, generating the enlarged detection range. Therefore, the CuO/Cu2O composite NFs electrode materials, with a multiple oxidation states system, would be promising candidates for the development of non-enzymatic glucose sensors.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...