Au–Fe/Ni alloy hybrid nanowire motors with dramatic speed†
Abstract
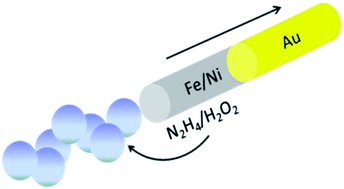
Au–Fe/Ni alloy nanowire motors, having an average length of 5.4 ± 1.2 μm and a diameter of 280 ± 10 nm, can move fast in a mixed fuel containing H2O2 and N2H4. The powered motion is attributed to the bubble thrust produced from catalytic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide on the Fe/Ni alloy segments, while hydrazine seems to act as a co-catalyst. The regulation of speed can be achieved by modulating the proportion of alloy composition, and the highest speed obtained is up to 850 μm s−1 (ca. 157 body-length per s), which is the fastest among all nanowire motors. Because of the ferronickel segment's magnetism, the Au–Fe/Ni alloy nanomotors also can be guided by the magnetic force, in addition to being controlled by the propelling force generated by the bubble thrust.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...