Electrochemical properties of an AgInS2 photoanode prepared using ultrasonic-assisted chemical bath deposition
Abstract
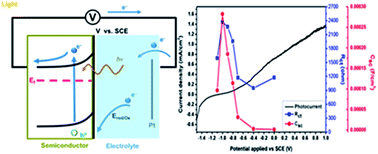
This study focuses on preparing a AgInS2 film electrode and studying its electrochemical properties. The AgInS2 film after 400 °C thermal treatment had the orthorhombic structure and a direct energy band gap of 1.98 eV. The thickness of AgInS2 film used in this study was 758.9 ± 40.9 nm. In order to understand the photoelectrochemical properties, electrochemical impedances of the AgInS2 photoanode in response to a light intensity of 75 mW cm−2 were scrutinized. It was found that homogeneous AgInS2 films were obtained with increasing coatings. In addition, these dense films can effectively suppress the dark current. Charge transfer resistance and space charge capacitance can be retrieved from impedance spectra by fitting the experimental data to the models. In fact, Randle's model fitted the data better than other complicated models. Under illumination, the space charge capacitance and charge transfer resistance are strongly correlated to the onset of the photo-enhanced current density, suggesting a direct carrier transfer to the electrolyte from the valence band of the semiconductor photoanode, rather than from the surface states.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...