New insight into the effect of the formation environment of ferrihydrite on its structure and properties
Abstract
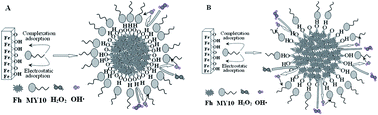
Ferrihydrite (Fh) is a naturally occurring nanoscale iron oxyhydroxide mineral. It is of great interest in soil science and environmental science due to its extremely high surface area and reactivity. In this work, Fh samples were prepared by three procedures (named Fh-1, Fh-2, and Fh-3). The formation of Fh-1 went through a pH change from acidic to neutral, and the formation of Fh-2 went through a pH change from alkaline to neutral, while Fh-3 was formed at a constant neutral pH. The three Fhs were characterized by high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM), terahertz (THz) spectroscopy, nitrogen adsorption isotherms, and low-temperature magnetic techniques. All these techniques indicate that the microstructure and formation process of Fh are strongly coupled. More importantly, the differences in microstructure among the three Fhs are reflected not only in their bulk structure but also in their surface properties. The adsorption and degradation of azo dye Mordant Yellow 10 (MY10) on the three Fhs were investigated. On the one hand, compared with Fh-1 and Fh-2, Fh-3 exhibits a high density of active sites per unit area, which leads to a large adsorption capacity. On the other hand, a strong affinity between Fh-3 and MY10 results in a more irreversible adsorption and a low degradation rate. The results from the current study shed new light on the synergetic effects of porosity and the variations of local structure on photocatalysis by iron oxide particles.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...