The electrochemical studies of cytochrome c incorporated in 3D porous calcium alginate films on glassy carbon electrodes
Abstract
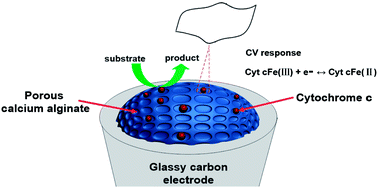
In this work, the cytochrome c (Cyt c) was incorporated in three-dimension (3D) porous calcium alginate (CA) films prepared by using sodium alginate, calcium chloride and polyethylene glycol, and formed the electroactive porous Cyt c–CA composite films. The stable composite films were characterized by means of scanning electron microscopy (SEM), UV-vis absorption, cyclic voltammetry (CV) and square-wave voltammetry (SWV) techniques. UV-vis experiments demonstrated that Cyt c assembled in the 3D porous CA films retains its near native conformation at medium pH. The Cyt c–CA films modified on glassy carbon electrodes showed a pair of well-defined and nearly reversible cyclic voltammetry peaks at about −0.352 V vs. SCE in protein-free buffer, which originated from heme FeIII/II redox couples within Cyt c. The electrochemical parameters such as apparent heterogeneous electron transfer rate constant (ks) and formal potential (Eo’) were estimated by fitting the data of SWV with nonlinear regression analysis. The Cyt c–CA films showed the electrocatalytic activity toward dioxygen, hydrogen peroxide, nitrite and trichloroacetic acid with significant decreases in the electrode potential required. Experimental data demonstrated that the porous film can provide a favorable microenvironment for the protein to directly transfer electrons with the underlying electrode and possess good stability and reproducibility, showing the possible future application of the films for biosensors and biocatalysis.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...