New organometallic ruthenium(ii) complexes containing chelidonic acid (4-oxo-4H-pyran-2,6-dicarboxylic acid): synthesis, structure and in vitro biological activity†
Abstract
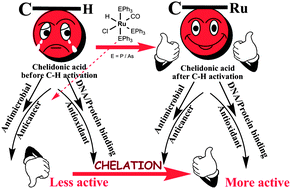
Two new bivalent organometallic ruthenium complexes [Ru(HL)(CH3CN)(CO)(PPh3)2] (3) and [Ru(HL)(CH3CN)(CO)(AsPh3)2] (4), (HL = 4-oxo-4H-pyran-2,6-dicarboxylic acid) were synthesized, structurally characterized and their biological activities (anti-microbial, DNA–protein interactions, antioxidant and cytotoxic activity studies (MTT, LDH release and NO release)) have been investigated and compared with that of appropriate precursor complexes [RuHCl(CO)(PPh3)3] (1), [RuHCl(CO)(AsPh3)3] (2) and the ligand H2L. The crystal structure of the complex 3 was solved by a single crystal X-ray diffraction technique, which revealed that it is a distorted octahedral with HL as a dibasic bidentate donor and the chelator was observed to undergo C–H activation at one of the ortho positions, leading to the formation of a five membered metallacycle. The in vitro antimicrobial activity was carried out using the well diffusion method against different species of pathogenic bacteria and fungi and complex 4 exhibited a better activity in inhibiting the growth of the tested organisms. DNA–protein interactions of the complexes have been examined by photophysical studies, which revealed that the complexes can bind with DNA through non-intercalation and the complexes strongly quench the intrinsic fluorescence of bovine serum albumin, through a static quenching process. The free radical scavenging ability, assessed by a series of in vitro antioxidant assays involving the DPPH radical, hydroxyl radical, nitric oxide radical, superoxide anion radical, hydrogen peroxide and a metal chelating assay showed that the new complexes 3 and 4 possess excellent radical scavenging properties over 1, 2, H2L, and the standard drugs, vitamin C and BHT. The in vitro cytotoxic activities of the compounds have been validated against A549 cells via an MTT assay, LDH release, NO release and the values were compared with that of the standard drug cisplatin. The results indicated that the new complexes, specifically the complex 3, displayed a higher cytotoxic activity in inhibiting the growth of A549 cells, outperforming by five fold, the standard drug cisplatin.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...