Microelectrode arrays based on carbon nanomaterials: emerging electrochemical sensors for biological and environmental applications
Abstract
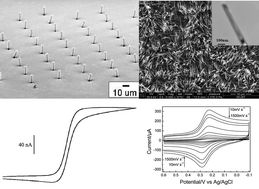
We present an overview of the recent advances pertaining to microelectrode arrays (MEAs) constructed from carbon-based nanomaterials, especially aligned carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and carbon nanofibers (CNFs). The electrochemical and chemical activities of carbon nanomaterials depend on the microstructures, especially the graphitic edge plane sites. This review focuses on the electrochemical behavior associated with the microstructures and arrangement of the MEAs. Coupling plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) with catalyst patterning techniques, low-density CNTs and individually addressable CNFs have been developed for multimode recordings with high temporal and spatial resolution. By introducing a nanowire core along the axis of CNFs to facilitate electron transfer, core–shell TiO2/C and TiC/C nanofiber arrays have been fabricated and exhibit inner core-dependent electrochemical behaviors. The TiC/C nanofibers show excellent electrochemical behavior due to good electrical contact as well as the conducting nanowire core that offers an ideal transport pathway for electrons. Applications of carbon nanomaterials to electrochemical sensors, ranging from biomolecules to inorganic ions from biological and environmental samples, are discussed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...