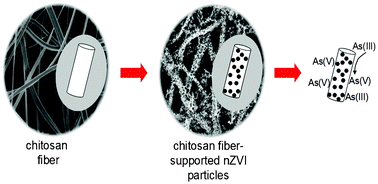
This study proposes a new sorbent for the removal of inorganic arsenic from aqueous solutions. Monodispersed nano zero-valent iron (nZVI) particles were nucleated at the surface of electrospun chitosan fibers (average fiber diameter of 195 ± 50 nm) by liquid phase reduction of FeCl3 using NaBH4. The material was characterized using SEM, TGA, XPS, XRD, and FTIR. The diameter of iron nanoparticles was found to vary between 75–100 nm. A set of batch experiments were carried out to elucidate the efficiency of the composite sorbent toward fixation of arsenite and arsenate ions. The ion concentrations in the supernatant solutions were determined using inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). The results revealed that the chitosan fiber supported nZVI particles is an excellent sorbent material for inorganic arsenic uptake at concentrations ranging from 0.01 to 5.00 mg L−1 over a wide range of pH values. Based on XPS analysis, As(III) was found to undergo oxidation to As(V) upon sorption, while As(V) retained its oxidation state. By virtue of the successful combination of the electrospun fibers' mechanical integrity and the large reactivity of dispersed nZVI particles, the applicability of the resulting sorbent material in arsenic sorption holds broad promise.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...