Structure and stability of complexes of charged structural units of heparin with arginine and lysine†
Abstract
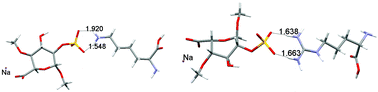
Our work reports in detail the results of systematic large-scale theoretical investigations of the complexes modeling heparin–protein interaction (CH3OSO3−⋯Arg+, CH3NHSO3−⋯Arg+, CH3CO2−⋯Arg+, CH3OSO3−⋯Lys+, CH3NHSO3−⋯Lys+, CH3CO2−⋯Lys+, CH3OPO3H2−⋯Arg+, CH3OPO3H2−⋯Lys+, CH3O(CH3)PO2−⋯Arg+, CH3O(CH3)PO2−⋯Lys+, 1,4-DiOMeIdoA2SNa−⋯Arg+, 1,4-DiOMeIdoA2SNa−⋯Lys+) using Becke3LYP and B97D levels of the density functional theory, as well as at MP2 ab initio method. Although initial geometries of complexes paired anionic and cationic species (ionic hydrogen bonds), full geometry optimization of isolated systems resulted in several cases with relaxed geometry and complexes stabilized via neutral hydrogen bonds. Hydration caused appreciable geometry changes, especially for substituents (carboxylate and sulphate groups) of the saccharidic part of the complex. The computed Gibbs energies ΔG° of the ionic hydrogen bond systems are negative and high (from −340 to −450 kJ mol−1). In complexes with neutral H-bonds the large destabilizing effect of entropy drives the association reaction to the left. However, owing to a sufficient enthalpy change Gibbs energies are indeed negative, but small (from −20 to 0 kJ mol−1) and the tendency to associate in gas-phase for the complex CH3OPO3H−⋯Lys+ is negligible. The phosphate anion in its complexes with arginine and lysine proved the lowest tendency to associate. Displacing of Na+ ions from heparine binding sites by protonated arginine and lysine molecules resulted in positive reaction energies. Solvent (water) reversed the reactivity. Reaction energies computed for the reactions conducted in water are calculated negative, i.e. water drives these reactions to the right.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...