Electrochemical behavior of steel/acid interface: adsorption and inhibition effect of oligomeric aniline
Abstract
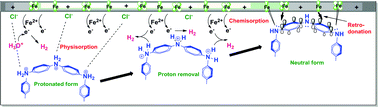
The present work shows the development of new protective oligomeric aniline (O-ANI) and its effect on electrochemical corrosion behavior of low carbon steel (LCS) in 1 M HCl at 308 K. The synthesized O-ANI was subjected to spectroscopic and electrochemical characterizations. The inhibition of LCS corrosion by O-ANI was studied using open circuit potential (OCP), potentiodynamic polarization (PDP), linear polarization resistance (LPR) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) measurements. The potentiodynamic polarization data indicated that O-ANI suppresses predominantly the cathodic process of corrosion reaction in comparison to the anodic process. The inhibition efficiency of the O-ANI depends on the length of the oligomeric chain and position of the functional groups. The spectra of all elements, within limits, on the steel surface was determined by energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX). Morphological changes on the electrode surface were monitored by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The thermodynamic parameters such as the adsorption equilibrium constant (Kads) and the free energy of adsorption (ΔG°ads) were calculated and discussed. Several adsorption isotherms were tested and the experimental data fitted well with the Langmuir adsorption isotherm. UV-visible spectral analysis of O-ANI solution containing LCS indicates the formation of Fe–N (ligand–metal) charge-transfer complex type interaction.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...