Fabrication and CO2 adsorption performance of bimodal porous silica hollow spheres with amine-modified surfaces
Abstract
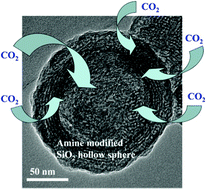
Carbon dioxide capture and storage (CCS) solutions have received enormous attention because CO2 is a primary greenhouse gas and plays a key role in global warming and climate change. In this work, bimodal meso-/macroporous SiO2 hollow sphere (BMSHS) samples with high specific surface areas were prepared by a hydrothermal method. Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) and perfluorododecanoic acid (PFDOA) were used as cotemplates and the CTAB/PFDOA weight ratio (R) was varied. The prepared samples were further modified with tetraethylenepentamine (TEPA), and characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), differential thermal analysis (DTA), thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA), and N2 physisorption techniques. This was followed by CO2 capture tests using a pure CO2 stream in the temperature range of 35–130 °C. The results showed that all of the prepared samples contained small mesopores with a peak pore size of ca. 3–4 nm and larger mesopores or macropores with a peak pore diameter of ca. 103 to 117 nm. The mesopores and macropores are from the shell and the cavity of hollow spheres, respectively. The R exhibited a significant influence on the specific surface area, as the specific surface areas increased with increasing R. All of the TEPA-modified samples exhibited good CO2 adsorption abilities, which were related to the amount of loaded TEPA, adsorption temperature, and the specific surface areas of the samples. A optimal amount of TEPA loading (about 50 wt%) and adsorption temperature (about 110 °C) were determined. The CO2 adsorption amount increased proportionally with the specific surface area. The maximum CO2 adsorption amount (4.41 mmol g−1 adsorbent) was achieved on the BMSHS sample prepared at R = 40 and TEPA loading of 50 wt%. The present study provides new insight into the design and synthesis of novel porous materials for CO2 capture.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...