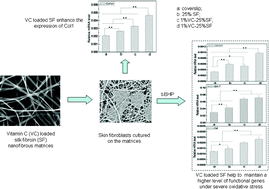
In this work, we reported on the preparation and skin benefits of L-ascorbic acid 2-phosphate (VC-2-p)-loaded silk fibroin (SF) nanofibrous matrices for the first time. The matrices was fabricated using a facile eco-friendly electrospinning processing. With a post treatment of 75 v/v% ethanol vapor, the structure of the matrices transformed from unstable silk I form into water-stable silk II. In vitro release studies confirmed VC-2-p disassociated from SF nanofibrous matrices easily. Both neat and VC-2-p-loaded SF nanofibrous matrices were beneficial to mouse fibroblast L929 cells (L929 cells) adhering, spreading and proliferating against cover slips. Whereas compared with neat SF nanofibrous matrices, VC-2-p-loaded SF nanofibrous matrices significantly promoted the expression of collagen type I alpha 1 (Col1a1), as evidenced by real time PCR. Subsequently, the oxidative injury model further verified both matrices aided L929 cells through antioxidation to survive from tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced oxidative stress (OS). Importantly, under severe OS, L929 cells on VC-2-p-loaded SF nanofibrous matrices maintained a higher mRNA level of Col1a1 as well as another two important functional genes, glutathione peroxidase 1 and catalase, than neat SF nanofibrous matrices. Our findings clearly indicated that the impressive skin benefits of SF nanofibrous matrices were further reinforced with the incorporation of VC-2-p, which implies the promising application of VC-2-p-loaded SF nanofibrous matrices in personal skin care and skin regeneration, including serving as wound dressings and anti-aging materials.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...