Access to bicyclic hydroxamate macrocycles via intramolecular aza-(4 + 3) cyloaddition reactions of aza-oxyallylic cation intermediates†
Abstract
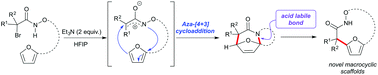
The intramolecular aza-(4 + 3) cycloaddition reactions of in situ generated aza-oxyallylic cations and furans have been reported for the construction of medium sized hydroxamate macrocycles. This method provides direct access to 12–18 membered bicyclic macrocycles. The highly functionalized macrocycles have been transformed easily in to a wide range of highly functionalized heterocyclic scaffolds including lactones and lactams that could serve the synthesis of complex macrocyclic natural products and pharmaceuticals.
- This article is part of the themed collection: HOT articles in Organic Chemistry Frontiers in 2016


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...