Non-covalent polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane-polyoxometalates as inorganic–organic–inorganic hybrid materials for visible-light photocatalytic splitting of water†
Abstract
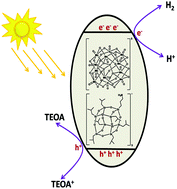
A new series of visible light responsive and water-stable inorganic–organic–inorganic hybrid materials such as polyoxometalate (POM) and polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes (POSS) with different metals was prepared, and these materials include {[PW12O40][(NH3CH2CH2CH2)(iBu)7Si8O12]3 (POM(W)–POSS), [PMo12O40][(NH3CH2CH2CH2)(iBu)7Si8O12]3 (POM(Mo)–POSS) and [PMo10V2O40][(NH3CH2CH2CH2)(iBu)7Si8O12]5 (POM(MoV)–POSS)}; these materials containing a cationic electron donor of amino-substituted POSS (POSS-NH2) on an anionic electron acceptor of POM have been developed for efficient and sustainable photocatalytic H2 production. It is interesting to note that the synthesized hybrid materials exhibit remarkable photocatalytic H2 production activities under visible-light irradiation. The maximum H2 production rate of 485 μmol h−1 g−1 is achieved using POM with heterometallic sites, i.e., (MoV)–POSS rather than that having homometallic sites. The enhanced photocatalytic H2 production is mainly due to improved charge carrier separation by electron-deficient metal sites and a red shift in the absorption, as revealed from photoluminescence and UV-vis spectra. Importantly, POM–POSS hybrid materials demonstrate excellent water stability during photocatalysis due to the hydrophobicity of the hybrid materials, which results from the integration of hydrophobic POSS-NH2 with POMs in contrast to free POMs. Additionally, the successful integration of POSS-NH2 into POMs is confirmed using FT-IR, NMR, ESI mass spectroscopy, and elemental and thermogravimetric analyses. The present study may open new possibilities in the design and development of stable POM organic/inorganic hybrid materials for solar energy conversion applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...